Sustaining Diabetes Control: The Superiority of Bariatric Surgery Over Conventional Methods
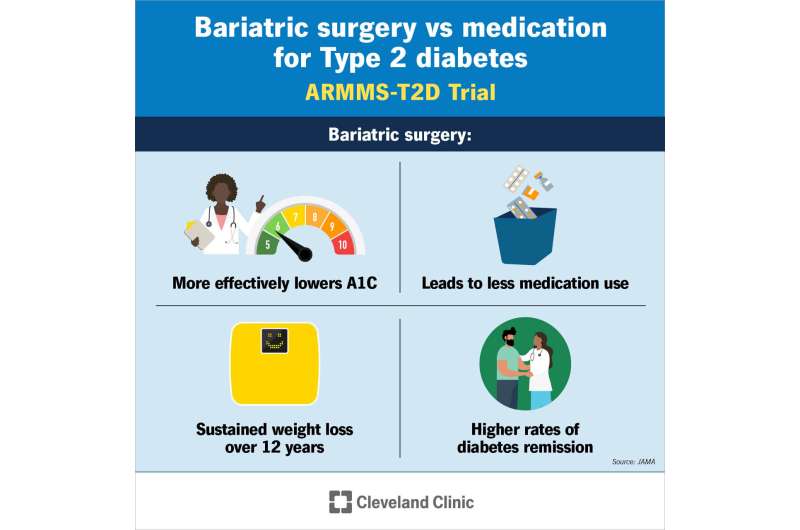
A landmark study, backed by the National Institutes of Health, has unveiled the superior long-term effectiveness of bariatric (or weight-loss) surgery in managing type 2 diabetes compared to the conventional approach of medication coupled with lifestyle modification. This extensive research, featured in JAMA, highlights how individuals with type 2 diabetes who opted for bariatric surgery not only showcased significantly better control of blood glucose levels but also enjoyed a higher likelihood of ceasing diabetes medication and achieving diabetes remission up to twelve years following the procedure. The study received funding from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK).
Dr. Jean Lawrence from NIDDK remarked on the procedure’s capacity to induce significant weight loss, thereby positively altering metabolic hormones. This alteration enhances insulin responsiveness and the ability to maintain optimal blood glucose levels. The study thereby confirms bariatric surgery as a transformative option for those grappling with obesity and type 2 diabetes, offering a path to long-term health improvement and an altered disease trajectory.
This follow-up study synthesized data from four separate single-center randomized trials across the United States. Originally conducted from May 2007 to August 2013, these trials assessed the efficacy of bariatric surgery against intensive medication therapy and lifestyle changes involving oral and injectable diabetes treatments. Notably, the investigation did not specifically explore GLP-1 agonists within the medical management strategies. The pooling of data from these studies aimed to provide a broader, more diverse examination of bariatric surgery’s efficiency, durability, and safety in treating type 2 diabetes.
The analysis included 262 participants from the initial studies, with 166 undergoing one of three distinct bariatric procedures and the remaining 96 subjected to medical and lifestyle management interventions. Noteworthy findings at the seven-year benchmark revealed the surgery group experienced an average weight loss of 20%, doubling the percentage seen in the medication/lifestyle cohort. More compelling was the superior blood glucose control in the surgery group, with 54% achieving an HbA1c level under 7%, compared to just 27% in the non-surgery group. Additionally, a significant reduction in the need for diabetes medications was observed within the surgery cohort, underscoring the lasting impact of the surgical intervention.
Extended follow-ups up to 12 years confirmed the persistence of these benefits. Further exploratory analysis identified even those with a lower BMI range (27-34) also reaped significant advantages in terms of HbA1c and weight loss from bariatric surgery, expanding the potential candidate range for this intervention.
Despite several advantageous outcomes, researchers noted a higher incidence of fractures, anemia, and gastrointestinal issues among the surgery group, hinting at potential nutritional deficiencies that necessitate ongoing monitoring post-surgery.
The study not only underlines the clinical advances made in combating obesity and type 2 diabetes but also stresses the positive ripple effect of public investment in such critical research areas. Through such endeavors, significant strides can be made towards enhancing the health and well-being of millions battling these complex conditions.







0 Comments